Outsourcing (BPO) – Risk Evaluation
Business Process Outsourcing is not a new idea, the first “outsource” deal was struck almost 40 years ago when it was termed “timesharing.” Today, it is more than merely outsourcing IT functions to an external supplier to provide application management or development for instance.
BPO covers anything that is not considered “core” strategy for a business, such F&A processes, HR, customer service and accounting & payroll. Since most business processes involve some form of automation, the term typically bandied nowadays is ITES-BPO or Information Technology Enabled Services.
Increasingly such services are offshored, the Philippines and India being the major recipients.
The perception is that the main reason companies outsource is to reduce or control costs. However, a recent Gartner survey found only about a third of companies achieved 80% of their expected cost savings. This statistical data supports the trend towards outsourcing decisions not being based on cost alone. Therefore, the reason to outsource should be based on business objectives with cost reduction being only one of these objectives.
Some of the business objectives identified by organisations that have successfully undertaken IT outsourcing activities include:
- Focus on core activities
- Bringing an out of control function back into organisational alignment
- Free up capital through reduced IT Infrastructure costs
- Flexibility in staffing and manpower management
Sounds good. Everyone should do it then? Well, no, not really. There have been many well documented instances where such solutions have gone horribly wrong and the fault does always lie at the foot of the supplier either. It makes sense then to look at all your options, and not just the bottom line, for that number is not entirely the one you will end up paying.
With this in mind, we wanted to share with you our recent experience. We were asked to provide a Risk Assessment Evaluation for a client late last year and had the opportunity to study four separate solutions for HR & Payroll services.
- The first was to deliver HR and Payroll services in-house using the clients hosted HR and Payroll system.
- The second was a fully outsourced option to an external provider including delivery, services and systems.
- The third was Software as a Service (SaaS) option, whereby the client delivered its HR and Payroll services in-house using an HR and Payroll system hosted and maintained by an external provider.
- And the fourth was a mixture of outsourcing the Payroll system, but keeping the delivery of the HR system in-house by either using the client’s hosted HR system or an externally hosted SaaS system.
Our process then went as follows:
What are the strategy drivers for a company to outsource?
Other than the four main perceived advantages listed above, the over-riding reason companies outsource is to reduce or control costs:
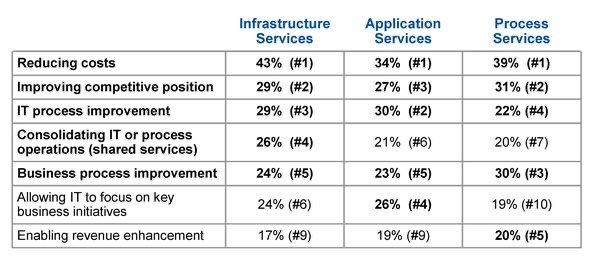
What are the critical success factors in outsourcing for business value?
Communication is the key to any successful relationship. For a successful outsourcing solution, the client needs to manage the supplier, not the supplier managing the client. Other factors are:
- On-going relationship management at the executive level
- Maintaining adequate quality controls
- On-going training
- Open and continuous lines of communication
- Understanding and addressing cultural divergence
- Client supplier management team
Why cost should not be the chief driver?
As mentioned, only 33% of firms surveyed by Gartner achieved 80% of expected cost savings. Therefore, any company looking to outsource must keep in mind the pros and cons of outsourcing before deciding to take the plunge.
“The InformationWeek Analytics 2010 Business of Outsourcing Survey, which shows that 6 of 10 IT shops outsource some critical function, also notes that almost 30% of those surveyed have fired an outsourcing partner in the last year. And a whopping 59% of respondents say that outsourced end-user support delivers lower quality than internal support, with 13% of those believing it’s more expensive as well, when all management and oversight costs are included.”
(http://www.ukrcham.ch/docs/Six_Key_Success_Factors_for_Outsourcing.pdf)
If not cost, then, what should the drivers for BPO be?
- Improving Service Levels
- Supplementing Staff and Resources
- Focusing on Core Business
- Reducing transactional costs
- Shortening implementation times
Assuming BPO is successful, what are the advantages?
- An outsourcing agreement will take care of non-core activities, such as administration and support operations, helping to put the focus back on the core functions of the business.
- It can reduce overhead costs that usually come with running support operations.
- It can free an organisation from investments in technology, infrastructure and people that make up the bulk of a support process capital expenditure.
- It creates business flexibility in staffing and manpower management, since the service provider is responsible for managing and maintaining the workforce.
What are the disadvantages of outsourcing?
- Companies risk of losing sensitive data and the loss of confidentiality. It is important, therefore, to have checks in place to avoid data loss.
- Losing management control of business functions mean that you may no longer be able to control operations and deliverables of activities that you outsource.
- Problems with quality can arise if the outsourcing provider doesn’t have proper processes and/ or is inexperienced in working in an outsourcing relationship.
- An outsourcing provider can often work with multiple customers. Therefore no single company gets priority which may result in delays and inaccuracies in work output.
- Hidden costs and legal problems may arise if the outsourcing terms and conditions are not clearly defined.
- Not understanding the culture of the outsourcing provider and the location where you outsource to may lead to poor communication and lower productivity.
So how does a company mitigate the disadvantages?
To mitigate the disadvantages of outsourcing, both parties need to work as one team with common goals. Each party needs to be transparent in the delivery of these goals. A “them and us” approach is a recipe for failure. If most of the responsibility is left in the hands of the provider, this creates a huge risk and almost certain failure. The provider will deliver what they think the client needs not what they actually need. We have seen this occur and it can be a very time consuming and painful process to get it back to an acceptable level. The client ends up with an inferior solution that they are stuck with or they will have to make an additional investment in improving the system to achieve a workable solution.
- Management Control
The loss of management control can be offset if good relationships have been put into place. Good relationship management will be determined by how well the two parties work with each other in sharing knowledge, specialised expertise, business processes and technologies. It needs to be a partnership.
- Quality issues
To mitigate the loss of control, it is necessary to monitor the provider’s performance and have quality assurance procedures in place. The business processes may be outsourced but the client is still responsible for them. They are still responsible for paying their employees correctly and in a timely manner. Resources will be required to carry out the validation and reconciliation of data. For a full BPO, we have found that additional resources are required for the stabilisation period which is about 6 months. However, this is dependent on the provider’s performance.
“The stabilization period typically lasts three to six months”
(www.pwc.com/us/en/point-of-view/assets/HR_Outsourcing_2.0.pdf)
- Communication Issues
Communication is the most important success factor, not only for an outsource solution but for any project. This is never truer than when you have a team of different cultures and where their first language is not English (or any other mother tongue). Co-location of the joint project team will assist in overcoming miscommunication by giving all members access to each other. Using the Agile method for a project, is an excellent way for the project team to communicate with each other, plus it eliminates the “them and us” mentality.
To assist this mitigation process, you also need a sourcing strategy and there are three primary steps necessary to develop one:
- Creating a BPO Baseline
Measure HR and Payroll in terms of cost and quality (service levels) defines your starting point.
- Identifying the Drivers/Reasons
Identifying and prioritising various drivers will feed business goals into the business case, help identify likely providers, give insights in terms of the most-appropriate contract structure and indicate the likely effects on the BPO relationship.
- BPO Delivery Approaches
Transform and Support
- A need to modernise or alter a current environment by partnering with a BPO provider that will take responsibility for the initial transformation and the ongoing operation of the revised environment.
- Vendor Responsibility
- The vendor agrees to assume responsibility for your ongoing operations (sometimes including the transfer of people and infrastructure) and also agrees to transform processes into a new, improved state over time.
“Companies considering business process outsourcing must look beyond the basics of the Sourcing Life Cycle and consider BPO-specific nuances. Failure to do so will make it difficult to judge the ultimate success, or failure, of a BPO relationship.”
(Published: 22 June 2005 ID:G00129338 Gartner Analyst(s): Lisa Stone )
What are the risks?
As part of the overall assessment and the risk assessment, the suppliers’ assumptions were reviewed for validity within the project initiation documents and the price schedules. The strengths and weaknesses of each supplier were identified and evaluated, then cross-referenced across each supplier to determine the overall risk by supplier and model.
The 3 areas of risk assessed were:
Estimation Risk
The risk is that any of the factors used to estimate the costs under any of the proposed models are flawed. The impact of the estimation risks is that the costs are underestimated.
Implementation Risk
Risk related to factors used to estimate the duration, complexity and components to enable the successful Implementation of the Project and bringing the system and Business Processes to a steady state under any of the proposed models. To mitigate these risks further, the following need to be managed with the assistance of the supplier:
- Planning
- Integration with other systems
- Change Management
- Transitional Management
- Communications
- Testing
- Training
Ongoing Risk
The Ongoing Risks are associated with maintaining the system over a given period, in this case 10 years, which will include patching and upgrades to both hardware and software and continuing integration to other systems. They are both external and internal with their own set of factors:
External Ongoing Risk – Risk Factors:
- External Ongoing Costs
- Basis for Ongoing costs vary e.g. Staff levels
- Additional Functionality requirements
- Change in required service levels
- Knowledge base deterioration of the client’s processes and procedures within the external provider due to external provider staff turnover
- Governance Costs
- Internal staffing levels.
- Additional Functionality requirements.
- Change in required service levels.
Internal Ongoing Risk – Risk Factors:
- Governance Costs
- Internal staffing levels.
- Additional Functionality requirements.
- Change in required service levels.
Cheatsheet to successful Outsourcing
So in conclusion, our evaluation threw up 8 key points businesses should follow in order to get the best out of any outsourced deal.
- Start with clear business-driven objectives for outsourcing
- Cost reduction alone is not a strong reason to outsource
- Strong Management team – Managers of successful outsourcing build a team with the competencies to manage the changes of the delivery arrangements over time. Without the capacity to lead in regard to your business needs, the provider will dictate what needs to change and when.
- Periodical review meetings – Regular review meetings are essential not only to resolve issues but to monitor and discuss any future changes to the delivery arrangement.
- Incentives and penalties around SLAs – Incentives are as important as penalties, as you want the provider to exceed expectations not just to meet them. Agreed Service Level Agreements should be enforced as not to make them worthless
- Training provider personnel – This is an ongoing necessity in order to maintain the provider’s knowledge in regard to a client’s business processes
- Understanding the cultural differences
Outsourcing arrangements are a long-term commitment. There is a need to understand cultural differences so that a foundation can be built between both to form a more effective working relationship.
Those of you keen to know the outcome of the evaluation and our subsequent model ranking, we have listed it below. Bear in mind not all businesses are the same but in this instance, this is what we suggested:
Model Ranking
The basis for the Model ranking was the more loss of knowledge, the higher the risk. If the Model is kept in house knowledge is retained. If a full BPO is undertaken and the knowledge transfer relies on training alone, the accumulated business knowledge is no longer accessible and the business relies on training as a compensatory factor. HR and Payroll resources have a high level of expertise within house which has a low turnover of staff and is more than capable of maintaining HR and Payroll processes to a high standard.
The Models have also been ranked in the following order from Low to High Risk.
1 Model 1: In-house solution
This was rated the lowest risk as it retained in-house expertise, knowledge of the current infrastructure and current business processes
2 Model 3: SaaS solution
This was rated second as in-house business processes are maintained. Outsourcing of the system creates Integration risks with remaining systems
3 Model 4: BPO Payroll only
This was rated third as HR business processes are maintained in-house whereas Payroll has been outsourced
4 Model 2 full BPO.
This was rated as the Highest Risk as all HR and Payroll business processes are outsourced along with the system


